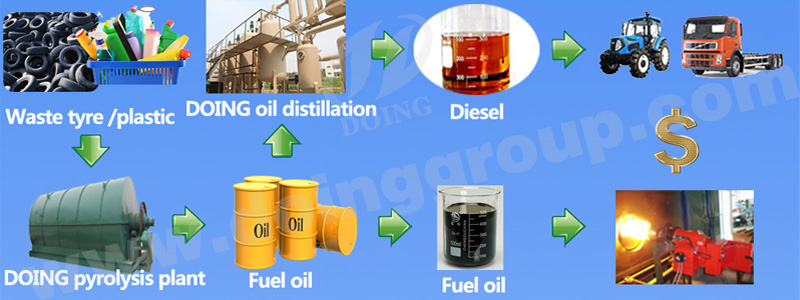
What is the advantage of fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant ?

The advantage of continuous waste tyre recycling plant
1.High capacity, which can process at least 10 tons waste tyre per day, up to 100 tons waste tyres per day;
2.Fully automatic with continuous feeding and discharge system;
3.PLC or computer control system, thus to save labour;
4.Multiple reactors design for fully pyrolysis to get high oil rate;
5.Indirect heating to prolong the usage life of the reactor;
6.Same as the batch type waste tyre recycling plant ,it’s also applicable to process waste plastics.
If you want to know more informations about our continuous fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant please feel free to contact us. We DONG Company has specialized in waste tyre recycling project for about 8 years, we would like to provide valuable informations and suggestions to help you implement this project.
- 1.High oil yield;no bad smell during process.
- 2.Enough safety systems;normal pressure.
- 3.Recycled tail gas to heating what is the advantage of fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant ?;no waste emission.
- 4.Auto welding to ensure what is the advantage of fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant ? life, service life will be 8-10years.
- 5.Excellent service(pre-service,selling service,after-sale-service).
Help customer do what is the advantage of fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant ? project plan,including financial analysis.
Help customer finished what is the advantage of fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant ? delivery,foundation,installation,trainning,commissioning and try running.
One year warranty period .
PREV: Waste tyre recycling machine in South America
NEXT:The end!
If you are intrested in investment what is the advantage of fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant ? ,or any other questions,such as project report,project cost,you can leave a message in below form, we will back to you once we got your message.
Leave a inquiry for what is the advantage of fully continuous waste tyre recycling plant ?: